Compute Module
A ztC Endurance system contains two compute modules![]() A customer-replaceable unit (CRU) located at the front of the ztC Endurance system. It is equipped with processors, RDIMMs, BIOS, BMC, fans, and other technology to boot and run the ztC Endurance system. Each system contains two compute modules.: compute module A and compute module B. Figure 1 shows the location of each compute module in a system.
A customer-replaceable unit (CRU) located at the front of the ztC Endurance system. It is equipped with processors, RDIMMs, BIOS, BMC, fans, and other technology to boot and run the ztC Endurance system. Each system contains two compute modules.: compute module A and compute module B. Figure 1 shows the location of each compute module in a system.
A compute module is a 2U component with processors, RDIMMs![]() Registered dual in-line memory module. RDIMMs have a register between the system’s memory controller and the dynamic random-access memory modules, thus allowing for greater capacity and increased reliability., BIOS
Registered dual in-line memory module. RDIMMs have a register between the system’s memory controller and the dynamic random-access memory modules, thus allowing for greater capacity and increased reliability., BIOS![]() The program a computer's microprocessor uses to start the computer system after it is powered on. It also manages data flow between the computer's operating system (OS) and attached devices, such as the hard disk, video adapter, keyboard, mouse, and printer., BMC
The program a computer's microprocessor uses to start the computer system after it is powered on. It also manages data flow between the computer's operating system (OS) and attached devices, such as the hard disk, video adapter, keyboard, mouse, and printer., BMC![]() Controller used for out-of-band monitoring and management of the ztC Endurance system. Each ztC Endurance system includes two BMCs; the primary BMC monitors the status of system components, even when system power is off.
BMCs are equipped with an Ethernet port that can be connected to the Stratus ActiveService Network (ASN). BMCs can communicate with the ASN even when the host operating system is unavailable. This allows remote management, and, if necessary, troubleshooting by the CAC or your authorized Stratus service representative over the internet., fans, and other technology to boot and run the ztC Endurance system.
Controller used for out-of-band monitoring and management of the ztC Endurance system. Each ztC Endurance system includes two BMCs; the primary BMC monitors the status of system components, even when system power is off.
BMCs are equipped with an Ethernet port that can be connected to the Stratus ActiveService Network (ASN). BMCs can communicate with the ASN even when the host operating system is unavailable. This allows remote management, and, if necessary, troubleshooting by the CAC or your authorized Stratus service representative over the internet., fans, and other technology to boot and run the ztC Endurance system.
Figure 3 shows an individual compute module. Each compute module provides:
-
Ports, including one VGA port and two USB 3.0 ports. See System Ports. (The UART USB-C connector, known as the debug port, is used only by Stratus Customer Service for debugging.)
-
An ID button, which activates the ID LED on the control-panel ear
 A module located at the front right of the ztC Endurance system. It houses a USB 2.0 port, power button for the ztC Endurance system, and LEDs that indicate system power status (PWR), fault conditions (ATTN), and module identification status (UID).. See Status LEDs.
A module located at the front right of the ztC Endurance system. It houses a USB 2.0 port, power button for the ztC Endurance system, and LEDs that indicate system power status (PWR), fault conditions (ATTN), and module identification status (UID).. See Status LEDs. -
An NMI
 A process, initiated when the system is not responding, where the system controller tries to restart the system by saving the contents of memory to a dump file, and then restarting the operating system. The interrupts are intended to keep all CPUs synchronized while the system controller attempts to resolve the problem. button. See Using the NMI Button.
A process, initiated when the system is not responding, where the system controller tries to restart the system by saving the contents of memory to a dump file, and then restarting the operating system. The interrupts are intended to keep all CPUs synchronized while the system controller attempts to resolve the problem. button. See Using the NMI Button. -
Status LEDs, which indicate the status of the compute module. See Status LEDs.
-
RDIMMs, which provide the system’s random-access memory (RAM). See Replacing and Adding RDIMMs.
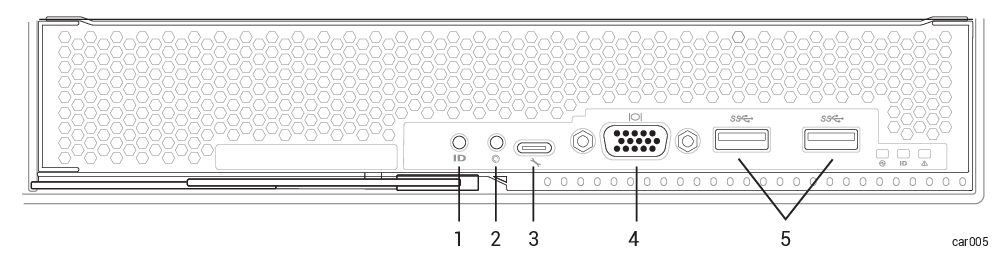
| 1 | ID button | 4 | VGA port |
| 2 | NMI button | 5 | USB 3.0 port (x2) |
| 3 | Debug port |